Sleep Apnea: Types, Risk Factors, and Treatment Options
Want to learn more about sleep apnea? This easy-to-follow guide breaks down what it is, why it happens, and what you can do to treat it.
What Is Sleep Apnea?
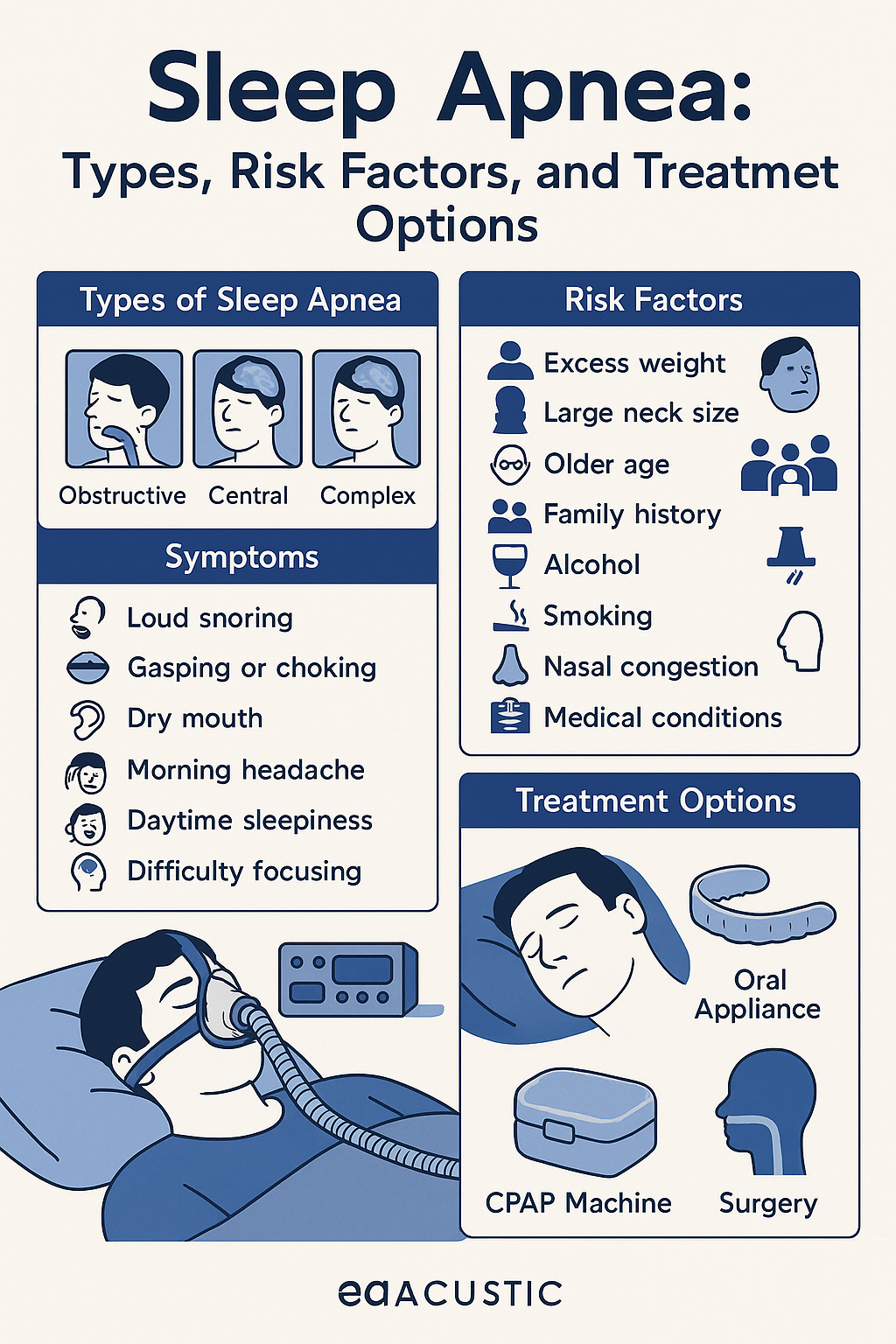
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder where your breathing stops and starts while you’re sleeping. This can happen many times during the night without you even knowing. It makes your sleep less restful and can lead to serious health problems if not treated. There are three main types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), central sleep apnea (CSA), and complex sleep apnea, which is a mix of both.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
Obstructive sleep apnea is the most common type. It happens when the muscles in the back of your throat relax too much. When this happens, your airway gets narrower or even closes while you try to breathe. Your brain notices the problem and quickly wakes you up to get you breathing again. You might not remember waking up, but it can happen many times during the night. You may also snore loudly, gasp, or choke in your sleep.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
Central sleep apnea is different because it’s not caused by a blocked airway. Instead, your brain forgets to tell your body to breathe while you’re asleep. This can cause you to stop breathing for short periods, which makes it harder to stay asleep and feel rested.
Complex Sleep Apnea
Complex sleep apnea is when you have both obstructive and central sleep apnea. It’s sometimes called treatment-emergent sleep apnea because it may show up when someone starts using a CPAP machine for OSA and then begins having symptoms of CSA too. This type needs careful treatment from a sleep doctor.
Common Sleep Apnea Symptoms
If you have sleep apnea, you might experience:
Loud snoring
Choking or gasping during sleep
Dry mouth or morning headaches
Trouble staying asleep
Feeling very tired during the day
Trouble focusing or remembering things
Moodiness or irritability
Even if you think you’re sleeping all night, these symptoms can mean you’re not getting the deep sleep your body needs.
Who Is Most at Risk for Sleep Apnea?
Risk Factors for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Being overweight – Extra fat around the neck can block your airway.
Thick neck – A thicker neck might mean a narrower airway.
Naturally narrow airway – Some people are just born with smaller airways.
Tonsils or adenoids – In children, large tonsils or adenoids can block airflow.
Gender – Men are more likely to have OSA, but women can develop it too, especially after menopause.
Age – Older adults have a higher risk.
Family history – Sleep apnea can run in families.
Alcohol or sedatives – These relax your throat muscles too much.
Smoking – Smoking can swell the airway and make breathing harder.
Chronic congestion – A stuffy nose can make things worse.
Other health problems – Like high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, or PCOS.
Risk Factors for Central Sleep Apnea
Older age
Being male
Heart problems like heart failure
Taking opioids or pain meds
Having had a stroke
How Is Sleep Apnea Diagnosed?
If you think you might have sleep apnea, start by talking to your doctor. They’ll ask you about your sleep habits and symptoms. If your partner hears you snore, gasp, or stop breathing during sleep, let your doctor know.
They might send you to a sleep specialist for a test called a sleep study. This can be done in a sleep lab or at home.
Sleep Study in a Sleep Center
In a sleep center, you’ll sleep overnight while machines monitor your heart, breathing, oxygen levels, and movements. These tests are very accurate and give doctors a clear picture of what’s happening during your sleep.
Pros:
Very accurate
Usually only need to do it once
Cons:
You have to sleep in a lab
Can be more expensive
At-Home Sleep Study
This is a simpler version of the lab test. You use a small device to measure your breathing and oxygen levels while sleeping at home.
Pros:
More comfortable
Less expensive
Cons:
Less accurate
May still need a follow-up test in a lab
Treatment Options for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
If your sleep apnea is mild, doctors may recommend simple lifestyle changes like:
Losing weight
Eating healthier
Sleeping on your side
Quitting smoking
For more serious cases, these treatments are available:
CPAP Machine
A CPAP machine gently pushes air into your throat through a mask, keeping your airway open. It’s very effective but may take time to get used to.
Auto-CPAP or BiPAP
These machines adjust the air pressure depending on how you breathe, which some people find more comfortable.
Oral Appliances
These are custom-made mouthpieces that keep your jaw in a position that helps you breathe better.
Surgery
Surgery is sometimes needed if other treatments don’t help. Kids often get their tonsils or adenoids removed. Adults may have surgery to shrink tissues, move their jaw, or create a new breathing hole in very serious cases.
Treatment Options for Central Sleep Apnea
Central sleep apnea is different from OSA, so the treatments are also different:
Treating underlying health issues like heart or nerve problems
Changing medications that may be causing breathing issues
Using a CPAP machine to ease breathing during sleep
Supplemental oxygen to give your lungs extra help
ASV machine – This advanced machine learns your normal breathing pattern and adjusts to help you breathe better. It works well for some but isn’t safe for people with heart failure.
Why Is Treating Sleep Apnea So Important?
Ignoring sleep apnea can lead to serious health problems. Here are just a few reasons why treatment is important:
Constant Tiredness
You might feel exhausted all day, which can affect work, school, and even your mood. It also increases the risk of car accidents.
High Blood Pressure
Sleep apnea lowers your oxygen while you sleep, which puts extra pressure on your heart and raises your blood pressure.
Heart Disease and Stroke
OSA can lead to serious heart problems, including irregular heartbeat, heart attacks, and strokes.
Diabetes Risk
Sleep apnea may raise your chances of developing type 2 diabetes or becoming insulin resistant.
Metabolic Syndrome
This condition includes high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and belly fat, and it increases the risk of heart disease.
Liver Problems
People with sleep apnea may have abnormal liver tests or liver damage.
Surgery and Medication Risks
OSA can make it dangerous to take some medications or go through surgery, especially under anesthesia.
Sleep Disruptions for Your Partner
Your snoring or gasping could keep your partner awake too, which may hurt both their sleep and your relationship.
Can Kids Get Sleep Apnea?
Yes, children can have sleep apnea too. It affects about 1 to 4 percent of kids, most often between the ages of 2 and 8. If untreated, it can cause problems like hyperactivity, poor focus, and even long-term heart issues.
A common sign in kids is loud snoring. If your child snores or shows signs of sleep apnea, talk to your doctor. Many children get better after having their tonsils or adenoids removed.
Sleep Apnea FAQs
What is the main cause of sleep apnea?
Obstructive sleep apnea is usually caused by blocked airways. Central sleep apnea happens when the brain doesn’t send the right breathing signals.
How do you fix sleep apnea?
Depending on the type and how serious it is, sleep apnea can be treated with lifestyle changes, a CPAP machine, a dental device, or surgery.
Is sleep apnea serious?
Yes, sleep apnea is a serious condition. It can lead to heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and many other health issues if not treated.
Do you think you might have sleep apnea? Don’t ignore the signs. Talk to your doctor and get tested so you can start feeling better, sleeping better, and living better.